-
- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
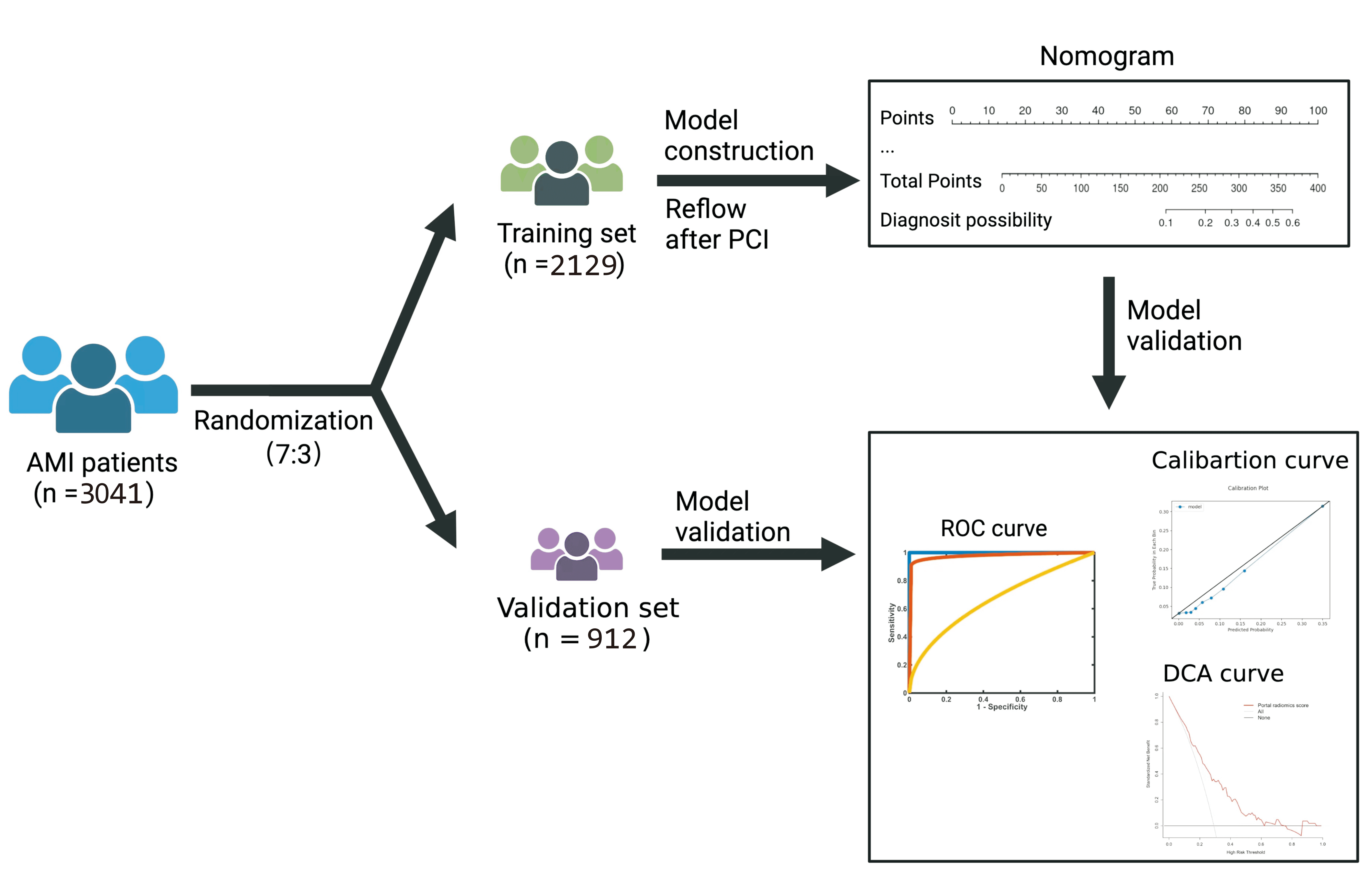
Background: The coronary no-reflow (NR) phenomenon is an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs). This study aimed to establish a clinical and comprehensive nomogram for predicting NR in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients after primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI). Methods: The multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the NR-related factors. A nomogram was established via several clinical and biochemical factors, and the performance was evaluated via discrimination, calibration, and clinical factors. Results: The study consisted of 3041 AMI patients after pPCI, including 2129 patients in the training set (70%) and 912 patients in the validation set (30%). The NR event was 238 in the training set and 87 in the validation set. The level of N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), basophil count (BASO), neutrophil count (NEUBC), D-dimer, hemoglobin (Hb), and red blood cell distribution width (RDW.CV) in NR patients showed statistically significant differences. In the training set, the C-index was 0.712, 95% CI 0.677 to 0.748. In the validation set, the C-index was 0.663, 95% CI 0.604 to 0.722. Conclusions: A nomogram that may predict NR in AMI patients undergoing pPCI was established and validated. We hope this nomogram can be used for NR risk assessment and clinical decision-making and significantly prevent potentially impaired reperfusion associated with NR.