- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
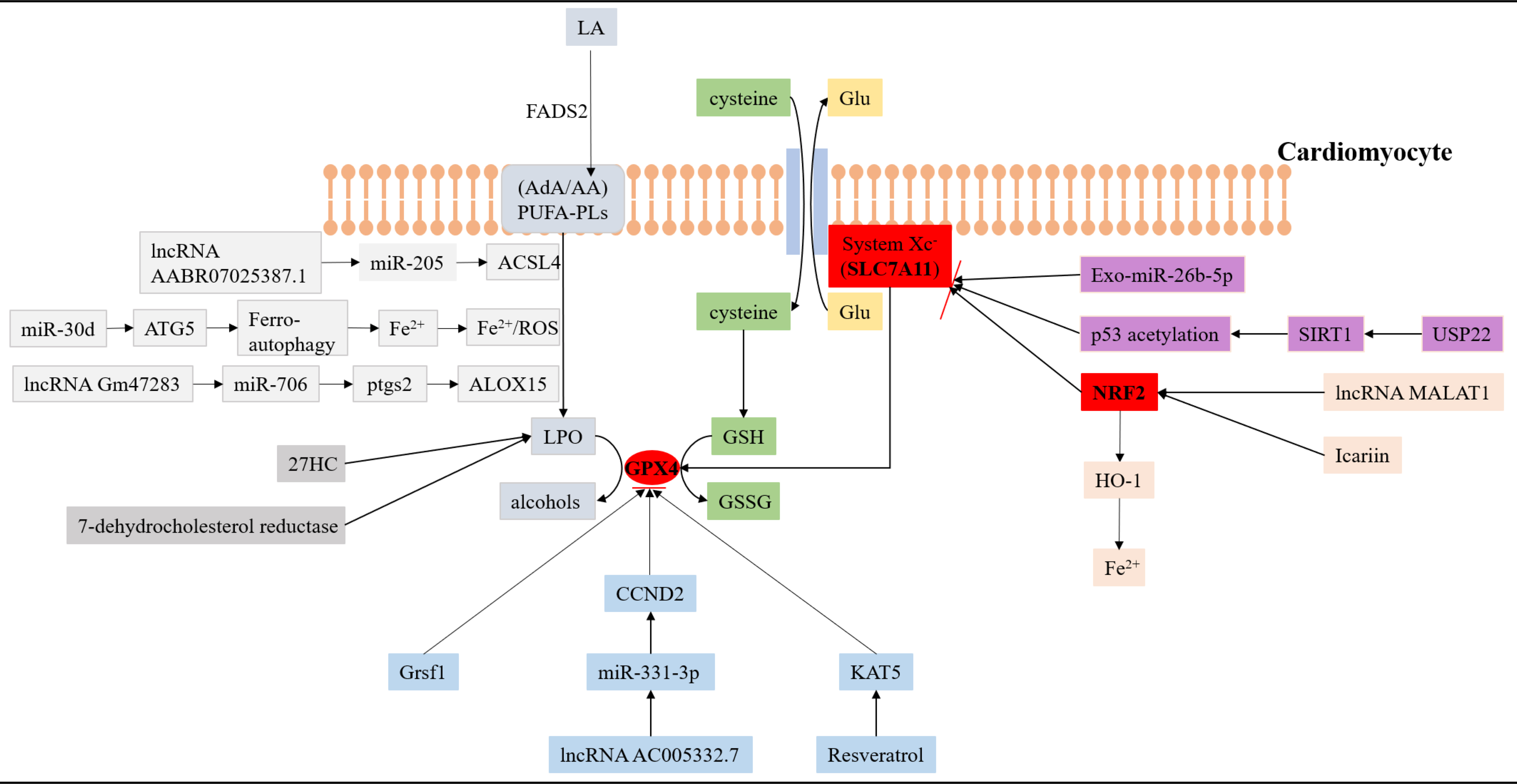
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is triggered by the blockage of coronary arteries, leading to restricted blood flow to the myocardium, which results in damage and cell death. While the traditional understanding of cell death primarily revolves around apoptosis, a new player in the game has emerged: ferroptosis. This novel form of cell death relies on iron and is propelled by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Lipid metabolism, an indispensable physiological process, plays a vital role in preserving cellular homeostasis. However, when this metabolic pathway is disrupted, the accumulation of excess waste increases, specifically lipid peroxides, which are strongly linked to the occurrence and progression of AMI. As a result, comprehending this complex interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism could pave the way for new therapeutic approaches in tackling AMI.