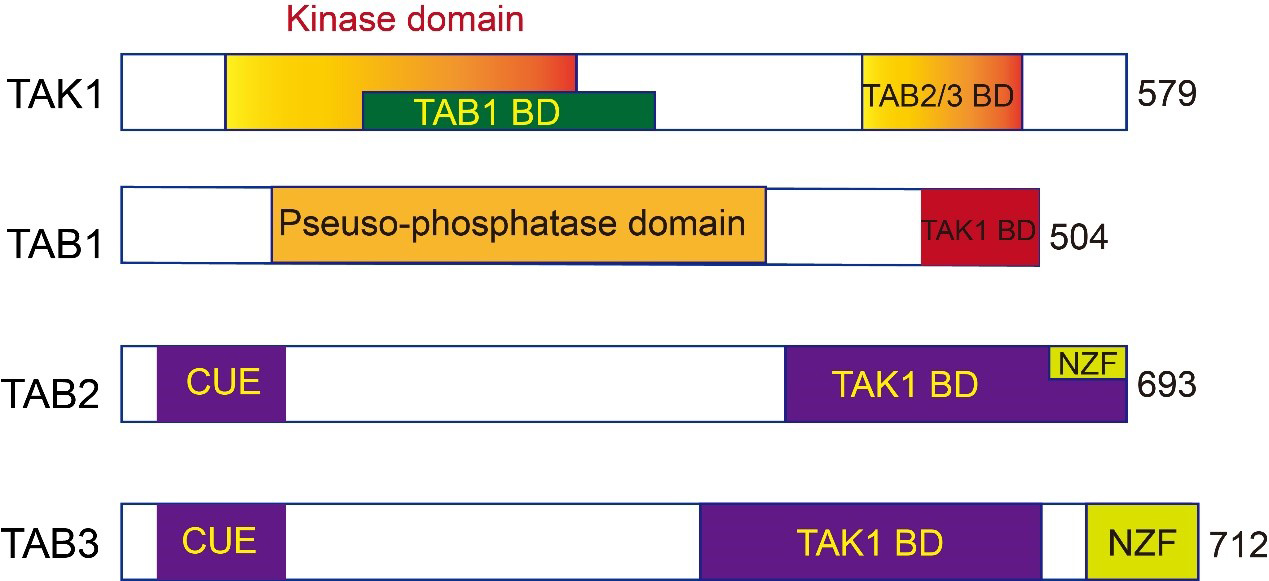
Fig. 1.Schematic illustration of the domain structures of human
transforming growth factor- (TGF-) activated kinase 1 (TAK1),
TAK1-binding proteins (TAB)1, TAB2, and TAB3. TAK1 contains a
kinase domain at the N-terminus, followed by a TAB1 binding domain (TAB1 BD) and
a TAB2/3 binding domain (TAB2/3 BD). TAB1 is characterized by a
pseudo-phosphatase domain and a TAK1 binding domain (TAK1 BD). TAB2 and TAB3 are
homologous proteins, and both have a CUE domain at the N-terminus, a TAK1 BD, and
an Npl4 zinc-finger (NZF) domain at the C-terminus. CUE, Coupling of Ubiquitin to ER degradation.